VOICE Complete (PDF)
File information
Author: Brunelle, Joshua S - Raleigh, NC - Contractor
This PDF 1.3 document has been generated by http://www.convertapi.com, and has been sent on pdf-archive.com on 13/08/2015 at 04:39, from IP address 65.190.x.x.
The current document download page has been viewed 1058 times.
File size: 2.65 MB (21 pages).
Privacy: public file



File preview
CCNA VOICE STUDY GUIDE
BY: Joshua S. Brunelle
Video 1 – Introduction
Equipment – CUCM Software, 2600xm Router gateway w/ VIC/nm-hd-zve card, 2801
Video 2 – Welcome to VOIP
Three separate networks – VOICE, DATA, and VIDEO
Why an organization would use VOIP?
Cost Savings
Moves, adds, and changes (High cost to add, move, and change)
Reduces Wiring
Reduces telecommuter and branch office expenses (PBX requires a tie-line between house and work)
VOIP allows you to connect via a VPN/Internet/ECT at lower cost
IT Staff Consolidation
Application consolidation
Toll bypass (free long distance)
Soft Cost Savings
Single inbox for messages (voicemail/fax/email)
Extension mobility ( Roaming profiles for phones) (user profile can be brought up on any phone)
Open architecture (Multi-vendor Solutions)
The Old to the New
Phase 1: Keep all existing PBX equipment, re-equip system with router that allows you to connect to WAN (VWIC)
Phase 2: scrapping PBX and going straight to VOIP
Video 3 – Unified Solutions overview
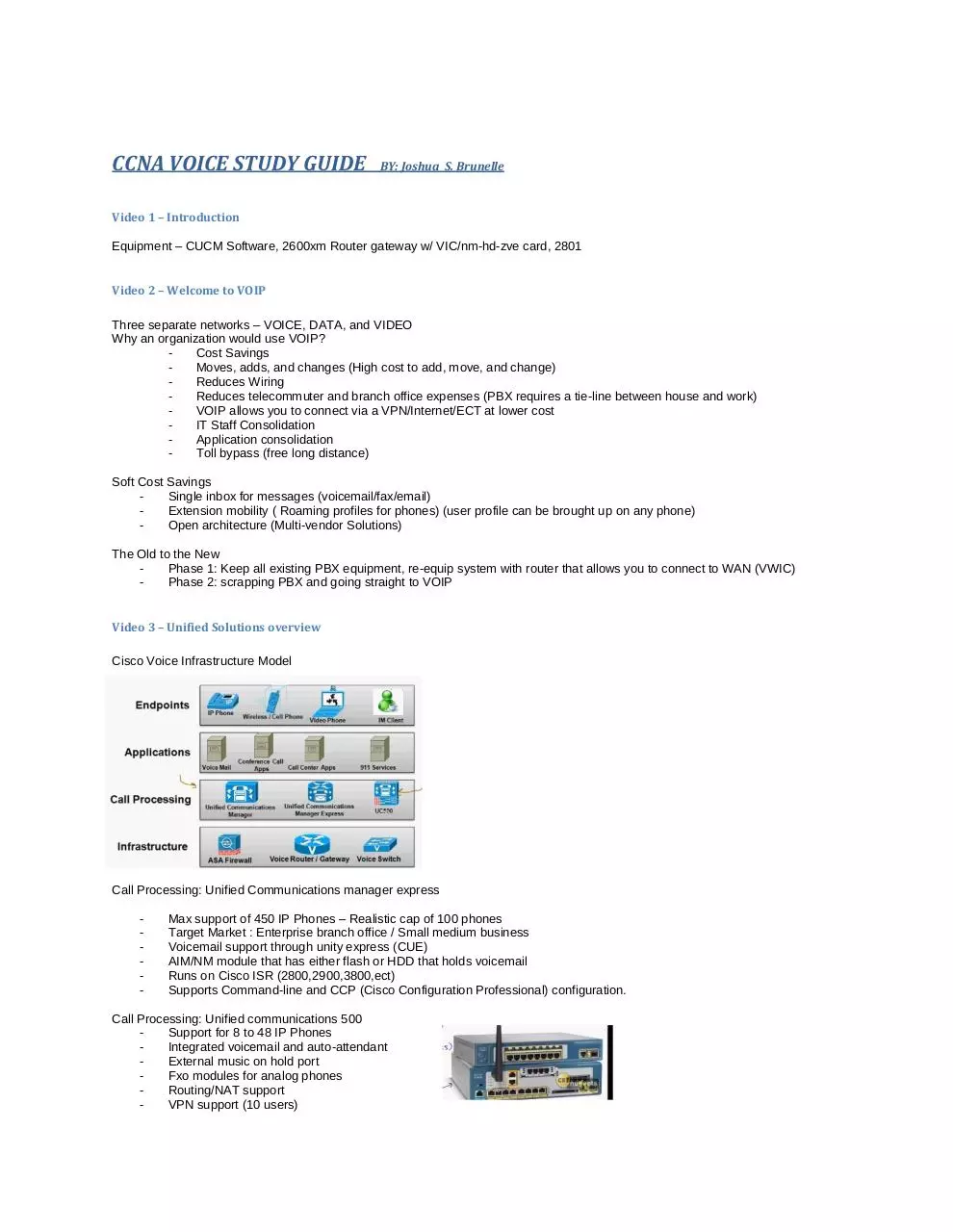
Cisco Voice Infrastructure Model
Call Processing: Unified Communications manager express
-
Max support of 450 IP Phones – Realistic cap of 100 phones
Target Market : Enterprise branch office / Small medium business
Voicemail support through unity express (CUE)
AIM/NM module that has either flash or HDD that holds voicemail
Runs on Cisco ISR (2800,2900,3800,ect)
Supports Command-line and CCP (Cisco Configuration Professional) configuration.
Call Processing: Unified communications 500
Support for 8 to 48 IP Phones
Integrated voicemail and auto-attendant
External music on hold port
Fxo modules for analog phones
Routing/NAT support
VPN support (10 users)
-
Optional 802.11 Wireless
Call Processing: Unified Communications Manager Business Edition
-
-
Provides scalability to 500 IP Phones
Combines 3 application
o
Cisco communications manager
o
Cisco Unity Connection
o
Cisco Unified Mobility
Great but no redundancy!
Call Processing: Unified Communications Manager
-
Scales to 60,000 IP phones per cluster
Failover on to other servers for redundancy
Multi-Site Support
Expensive
Video 4 - Unified Solutions Overview:
Cisco Voicemail Options : Unity
-
Runs on a windows platform, fully integrates into MS exchange and lotus domino
Painful to set up
Still has unique features but fading quickly
Currently 15,000 users per server
Cisco Voicemail Options: Unity Connections
-
Linux based appliance
Previously “Imap-Only” integration now integrates with MS exchange
20,000 users per server
Unlimited number of telephony integrations
Cisco Voicemail Options: Cisco Unity Express
-
Voicemail options integrated w/ cisco CME
AIM and NM form Factors
Up to 250 Users
Basic interactive voice response
Auto Attendant, email (exchange) integrations.
Understanding Cisco Presence
-
Provides status information
Integrates into nearly every IT faces (CUCM, IP phones, Unity, LDAP Server, etc)
Uses industry stander SIP to collect data
Integration with personal communications
Enterprise IM
Video 5 – Historic Voice:
Loop-start – When a signal received to a phone when the handset it picked up
Glare – calls get bridged by accident
Ground start- grounds ring line to signal that it needs a dial-tone
Analog Signaling: Supervisory Signal
On-hook – disconnects circuit
Off-hook – connects circuit
Ringing – Uses A/C rather than DC to not require a return line to trigger ringing
Analog Signaling: Information Signal
-
Dial Tone
Busy
Ring back
Congestion
-
Re-Order
Receiver off hook
No such number
Confirmation
Analog Signaling: Address Signal
-
Pulse – uses broken / connected to signal numbers
Dual tone multi-frequency – different sound frequencies to enter numbers
Video 6 – History Voice Continued:
Problems with analog connections
Distance limitation - signals degrade over distances, and require a repeater
Wiring requirements – High wiring requirements
Digitizing Voice –
Sample the signal.
Perform Quantization on the Sample
Convert the sample into binary
Compress the Samples
PCM – Pulse Code Modulation
Compress – Send just the changes, builds a codebook
Video 7 - Modern Voice:
Call Control Models: Distributed
Call manager express routers (CME)
Phone tells router that they dialed a #
CME looks at route table to find # in their database
Call Control Models: Centralized
Routers are used to direct IP phones to the call manager
Which is used as the brains of the VOIP system.
Drawback – Redundancy
Catching the Key Protocols
Signaling Protocols
H.323
MGCP
SIP
SCCP
Streaming Protocols
RTP (Real Time Transport Protocol)
RTCP (Real Time Transport Control Protocol) - Call statistics
Campus IPT Design
Single Site – Easiest
All call Managers in one location.
Central- Site Deployment Design
Router links to remote sites via
WAN & PSTN
Video 8 - Network Foundation - Preparing the Infrastructure for VOIP:
Network Foundations:
Key roles of catalyst switches:
Provide power over Ethernet (POE)
Dual VLANs / Voice VLANs/ Aux VLANs
Class of service (COS) / Quality of service (QOS) – ability to prioritize vlan (voice traffic) over other traffic
How you can power a phone
Inline power
o
Cisco Pre-Standard POE
o
IEEE 802.3AF
Midspan Power – (power patch panel) – Sits in between switch and device and plugs into a power source
o
Benefit being that you do not have to replace switch with one that is POE
Wall Power
#Show Power Inline
Delay power shut off for
Phone that reboot when
They are plugged in.
# Power inline delay shutdown
Video 9 – Preparing the Infrastructure for VOIP, Part 2 –
Cisco IP Phone Boot Process
1. Cisco Switch detects PoE capabilities
2. Switch sends vlan via CDP
3. IP Phone receives DHCP request including option ISO
4. IP phone contacts TFTP server, receives configuration file.
5. IP phone registers with cme router.
Configuring DHCP services on router:
Exclude any necessary IP addresses
Create DHCP Pool
Define network
Define default router (gateway)
Define DNS settings
Configure IP Helper-Addresses, if necessary.
Show which devices have received IP via DHCP – Show IP DHCP binding
Setting Clock
Configure NTP
1.
Configure NTP Server
#Ip name-server 4.2.2.2 or 8.8.8.8
#ntp server “SERVER NAME”
#Conf t
#Clock Timezone NORTH CAROLINA -8
2.
Optionally, Configure one or more of your devices as NTP masters.
#ntp master
Video 10 – Getting familiar with Administration:
CME Administration Options
o
IOS Command Line
o
CME Graphic interface from router flash
o
Cisco Configuration professional
Core Commands of CALL MANAGER EXPRESS –
#Show ephone registered – Shows details on IP phones on network as well as directory number
#Show run | Section Ephone-dn - Shows phones directory #
Epone manages phone
Ephone-dn manages #s
CME Command-Line
o
Old GUI that is being phased out
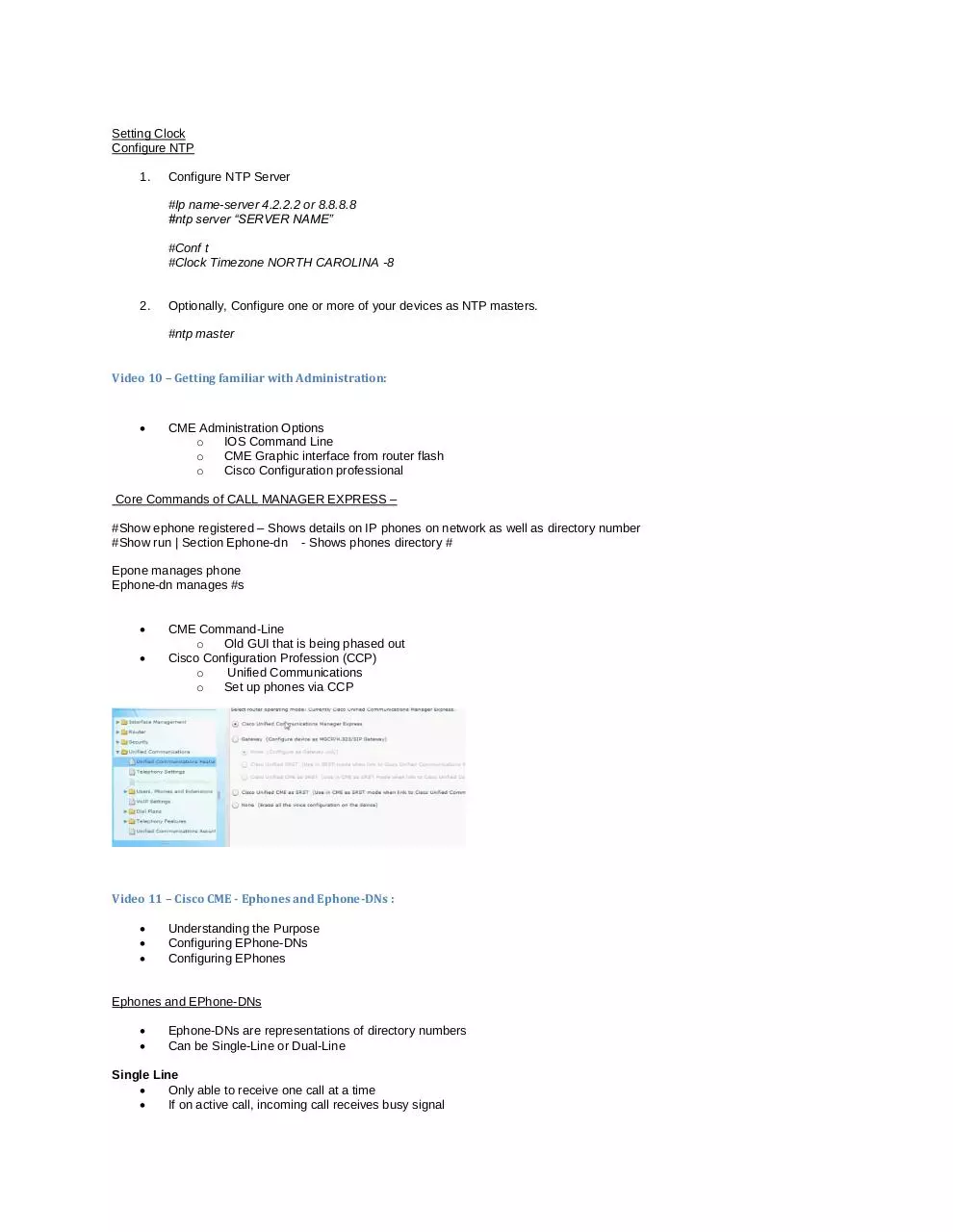
Cisco Configuration Profession (CCP)
o
Unified Communications
o
Set up phones via CCP
Video 11 – Cisco CME - Ephones and Ephone-DNs :
Understanding the Purpose
Configuring EPhone-DNs
Configuring EPhones
Ephones and EPhone-DNs
Ephone-DNs are representations of directory numbers
Can be Single-Line or Dual-Line
Single Line
Only able to receive one call at a time
If on active call, incoming call receives busy signal
Useful for paging lines
Dual Line
Handles two call simultaneous calls
Necessary for call waiting, conference calling, consultative transfers
Configuring EPhone DNs
In CME
#Ephone-DN 1 Dual-Line
Or
#Ephone-DN 1 -for single line
#(Config-ephone-dn)# Number 1002 Extension is 1002
Understanding Ephones
Are linked to the device by the Mac
o
Printed on the box
o
Printed on the back of the IP Phone
o
From setting > network configuration menu of IP Phone
Adding Phones via Mac
#Ephone 1 Dual-Line
#(Config-ephone)Mac-Address 0000.0000.0000.0000
1.
2.
3.
Create necessary Ephone-DNs
Create Necessary Ephones
Associate Ephone and Ephone DNs using the mystical BUTTON commands
#button ?
Sets up the phone # assignments for the buttons on the IP Phone – Link buttons to Ephone-DNs
Video 12 – Cisco CME - Ephones and Ephone-DNs, Part 2 :
Example:
#button 3b5 <- Button 3 will show phone 5. if phone 5 calls it will have no ring, and call waiting beep.
Shared lines receive calls at the same number randomly
Preference and huntstop command
Preference command:
#PREFERENCE 0 <- Most desirable
The only time phone 2 would get a call is if they first phone was already in a call.
The Huntstop Command:
#preference 0
#Hunstop Channel
#no hunstop
Understanding Shared lines and button overlay
Call 1010 extension and all 3 phones would ring.
#Ephone-DN 10
#number 1010
#preference 0
#no huntstop
#ephone-dn 11
#number 1010
#preference 1
#exit
#ephone 8
#button 1010,11
#exit
Understanding Auto-Registration and Assignment
By default, CME registers any Ephone (can be disabled
#conf t
#Telephony-service
#no Auto-register-ephone
#restart all restarts all phones
Auto-Assignment associates
Video 13 – Cisco CME – Management Using the Cisco Configuration Profession:
What is the CCP? How do I set it up?
Managing Users, Endpoints, and DNS with CCP
Managing CME Features with CCP
o
Easier way of creating phones and extensions via
a graphic interface.
You can add display names, users, passwords, ect…
Video 14 – Management using CCP, Part 2 – Features:
Managing CME features with CCP
o
Phone directory
o
Intercom
o
Forwarding
o
Transfer
o
Call park
o
Call Pickup
o
Paging
o
After hours restrictions
o
Single Number reach
Phone Directory – Manually add items to directory like Fax machines
Configure>Unified Communications>Telephony Features> Directory Services
Forwarding
Configure>Unified Communications>Users, Phones and Extensions> Extensions
Toll Fraud via transferring calls to long distance numbers.
Settings:
Transfer Pattern – Advanced Telephony Settings>
Call Park
Configure>Unified Communications>Telephony Features>Call Park
Create Call Park Entry
Call Pickup
Configure>Unified Communications>Telephony Features>Call Pickup Groups
Allows you to answer another ringing phone
Intercom
Configure>Unified Communications>Telephony Features>intercom
Automatically connects to the other phone with a one way voice.
Create>
Select first and second user and set the settings.
Paging
Configure>Unified Communications>Telephony Features>paging numbers/groups
Enables you to page a group of people or a group of groups
After Hours Restrictions
Configure>Unified Communications>Telephony Features>After-Hour Toll bar
You can add weekly schedules that call are blocked during
Blocking different call patters *ie. Calls starting with 111
Blocked during holiday schedule
Single
Configure>Unified Communications>Users, Phones and Extensions> Extensions
>Edit Extension> Advance Tab> Single Number Reach
Set up number of the one other device that will be called with the extention.
Video 15 – Gateways and Trunks:
Understanding Voice CODECs
Reviewing the digital conversion process
Common audio CODECS
Determining CODEC bandwidth
Common Audio CODECs
MOS Scale – Quality rating score from 1-5
G.729 #1 CODEC for Cisco
Choosing a CODEC and Sample Size
G.711 –
Sample size dictates the amount of audio included in each packet (default 20ms)
Larger Samples = Bandwidth savings
Larger Samples = More delay
Bytes per sample = (Sample_size X Codec_bandwidth)/8
#Conf t
#Dial Peer Voice 50 voip
#Codec ?
VOIP Bandwidth Savings Measures
Voice Activity Detection (VAD): Suppresses silence in the conversation - Average of 35% bandwidth savings
Compressed RTP: Compresses Network and Transport layer headers from 40bytes to 2-4 bytes
o
Bandwidth savings CODEC dependent (around 40% savings with 6.729 CODEC)
o
Processor intensive task
Understanding and using DSP Resources
DSP – DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCCESSOR
Digital Signal Processors (DSPS) offload media processing function from voice processing equipment
Media Processing
o
Coding
o
Transcoding
o
Media Termination Point (MTP)
o
Conferencing
CODEC Complexity: Converting Voice to Packets
DSPs are limited in the number of calls they can handle
Two DSP Forms:
o
C549 DSP
o
C5510 DSP
Two Levels of CODEC Complexity:
o
Medium (G.711, G.726, G.729A, G.729AB
o
High (G.723, G.728, G729, G.729B)
RTP AND RTCP
Download VOICE Complete
VOICE Complete.pdf (PDF, 2.65 MB)
Download PDF
Share this file on social networks
Link to this page
Permanent link
Use the permanent link to the download page to share your document on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, or directly with a contact by e-Mail, Messenger, Whatsapp, Line..
Short link
Use the short link to share your document on Twitter or by text message (SMS)
HTML Code
Copy the following HTML code to share your document on a Website or Blog
QR Code to this page

This file has been shared publicly by a user of PDF Archive.
Document ID: 0000294952.