Med Gen Unit 2 all powerpoints (PDF)
File information
Title: Introduction to Biology 2
Author: Nicole Evans
This PDF 1.3 document has been generated by http://www.convertapi.com, and has been sent on pdf-archive.com on 28/02/2015 at 23:09, from IP address 24.1.x.x.
The current document download page has been viewed 1067 times.
File size: 11.41 MB (274 pages).
Privacy: public file



File preview
AUTOSOMAL DOMINANCE
AND RECESSIVE INHERITANCE
Biol 59500
2.11.15
1
OBJECTIVES
For now, we will focus on the single-gene disorders
caused by mutations on the autosomes
Patterns of inheritance
Factors that complicate inheritance patterns
Molecular mechanisms that cause genetic
disease
Risks of transmitting single-gene diseases
2
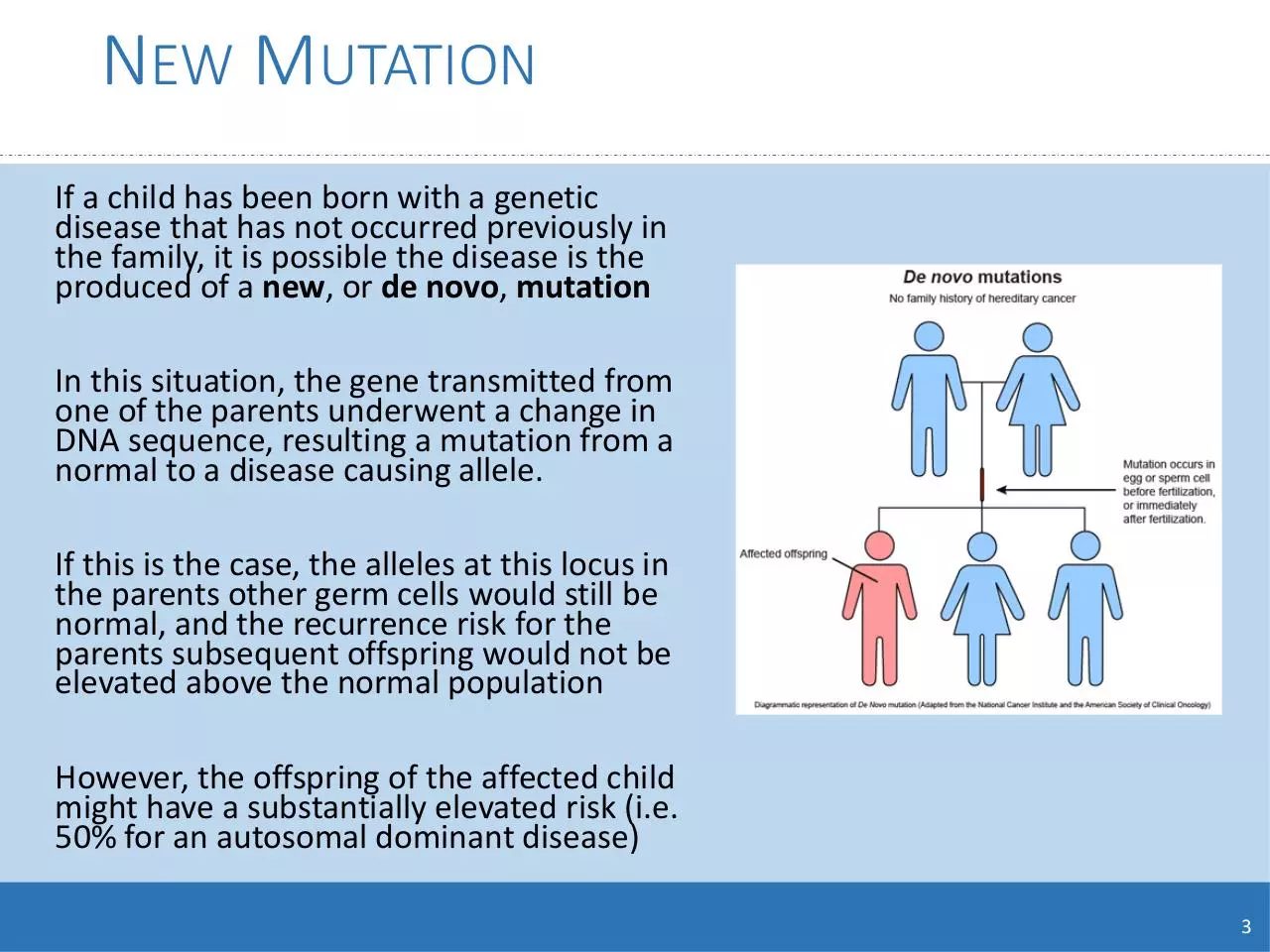
NEW MUTATION
If a child has been born with a genetic
disease that has not occurred previously in
the family, it is possible the disease is the
produced of a new, or de novo, mutation
In this situation, the gene transmitted from
one of the parents underwent a change in
DNA sequence, resulting a mutation from a
normal to a disease causing allele.
If this is the case, the alleles at this locus in
the parents other germ cells would still be
normal, and the recurrence risk for the
parents subsequent offspring would not be
elevated above the normal population
However, the offspring of the affected child
might have a substantially elevated risk (i.e.
50% for an autosomal dominant disease)
3
NEW MUTATION
A large fraction of observed
autosomal dominant diseases
are the result new mutations
For example, it is estimated
that 7/8 of all cases of
achondroplasia are caused by
new mutations and only 1/8
are inherited
This is primarily because the
disease tends to limit the
potential for reproduction
4
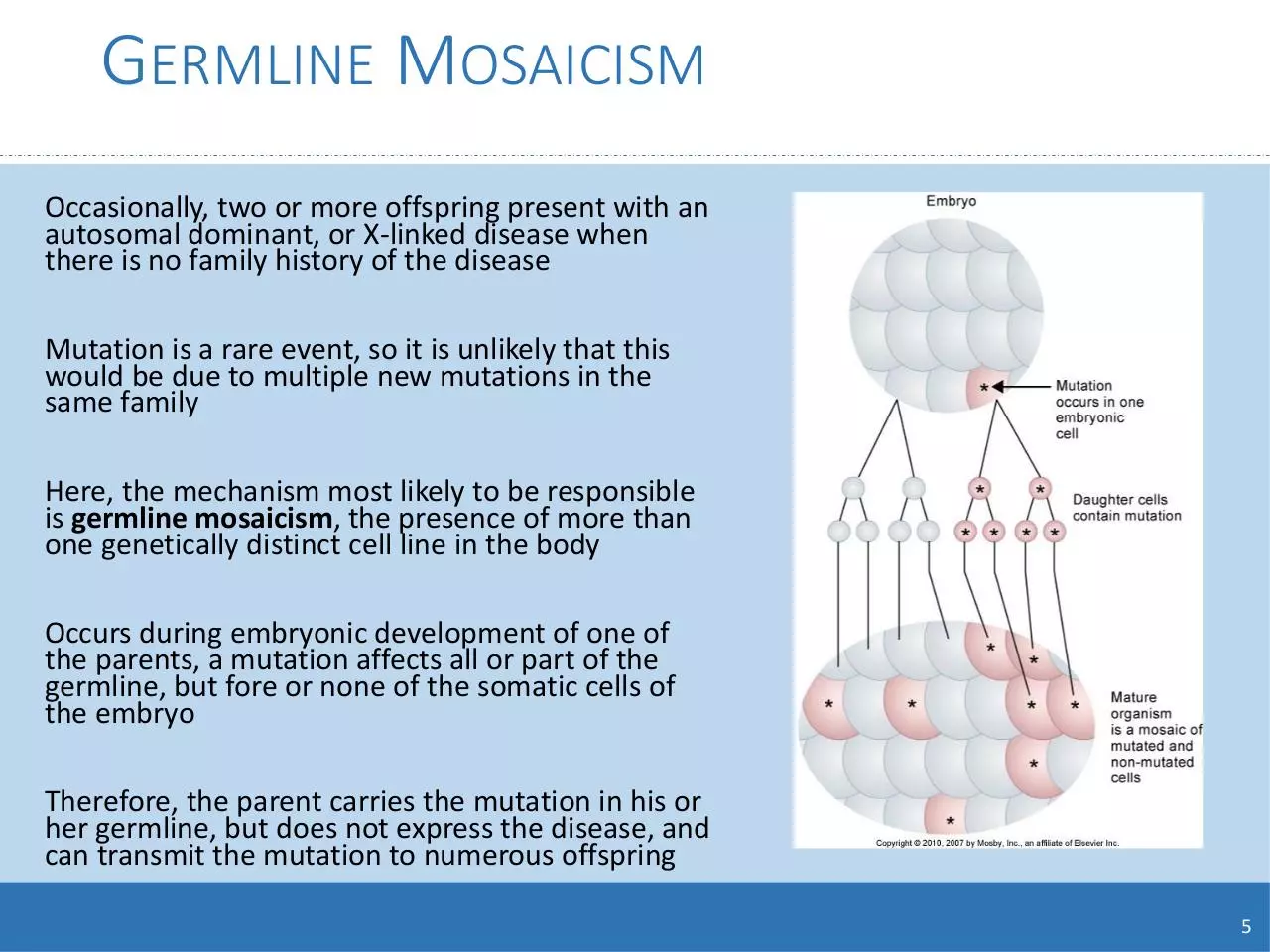
GERMLINE MOSAICISM
Occasionally, two or more offspring present with an
autosomal dominant, or X-linked disease when
there is no family history of the disease
Mutation is a rare event, so it is unlikely that this
would be due to multiple new mutations in the
same family
Here, the mechanism most likely to be responsible
is germline mosaicism, the presence of more than
one genetically distinct cell line in the body
Occurs during embryonic development of one of
the parents, a mutation affects all or part of the
germline, but fore or none of the somatic cells of
the embryo
Therefore, the parent carries the mutation in his or
her germline, but does not express the disease, and
can transmit the mutation to numerous offspring
5
GERMLINE MOSAICISM
Germline mosaicism has been studies extensively in
the lethal perinatal form of osteogenesis
imperfecta (OI type II), which is caused by
mutations in type 1 procollagen genes
Identified families in which unaffected parents
produced multiple offspring affect with this disease
PCR of one of the fathers DNA demonstrated that a
gene mutation was not present the fathers
fibroblasts, but was present in one of every 8 of his
sperm cells
Germline mosaicism has also been observed in
achondroplasia, neurofibromatosis, Duchenne
muscular dystrophy (15% of cases), and hemophilia
A (20% of cases)
6
REDUCED PENETRANCE
Another important
characteristic of many
genetic diseases is reduced
(or incomplete) penetrance
Here, a person may have the
disease-causing genotype
and not exhibit the disease;
however, he or she can
transmit the disease causing
mutation to the next
generation
7
REDUCED PENETRANCE
For example, Retinoblastoma, a malignant eye tumor, is an autosomal
dominant disorder with reduce penetrance.
Retinoblastoma is a the most common childhood eye tumor (1 in 20,000
children).
The tumor typically develops between 3 months after conception and 4
years of age, and nearly always presents clinically by age 5.
8
REDUCED PENETRANCE
Family studies have shown
that about 10% of the
obligate carriers of
retinoblasma-causing
mutations (those who have an
affected parent and affected
children, and therefore must
carry the mutation)
The penetrance of the
genotype is said to be 90%
9
Download Med Gen Unit 2 all powerpoints
Med Gen Unit 2 all powerpoints.pdf (PDF, 11.41 MB)
Download PDF
Share this file on social networks
Link to this page
Permanent link
Use the permanent link to the download page to share your document on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, or directly with a contact by e-Mail, Messenger, Whatsapp, Line..
Short link
Use the short link to share your document on Twitter or by text message (SMS)
HTML Code
Copy the following HTML code to share your document on a Website or Blog
QR Code to this page

This file has been shared publicly by a user of PDF Archive.
Document ID: 0000211925.